The Inflammation and Weight Gain Connection
Do you find yourself gaining weight without explanation? It could be due to inflammation in your body.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the connection between inflammation and weight gain is key to creating a healthier lifestyle to shed those unwanted pounds.
This blog post will discuss the connection between inflammation and weight gain, the triggers of inflammation in your body, and how you can reduce inflammation to get back on track.
What is Inflammation?
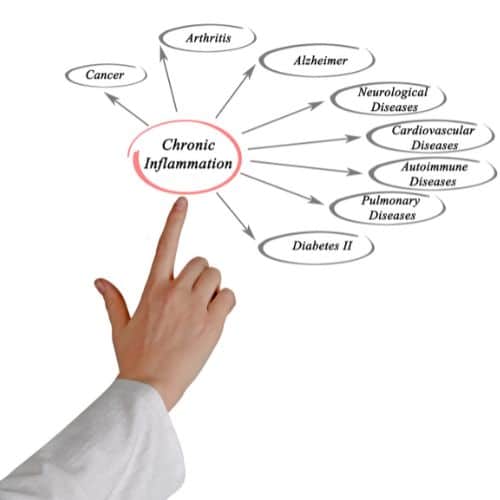
Inflammation is an important tool to help the body heal from injury or infection, but when it is chronic, it can cause damage to the body.
A number of factors, including poor diet, a sedentary lifestyle, toxins, disease, and stress, can cause chronic inflammation. This type of inflammation can last months and even years.
How Does Inflammation Lead to Weight Gain?
The connection between inflammation and weight gain is complex, but the underlying cause is an imbalance in hormones that regulate hunger, energy expenditure, and metabolism.
Chronic inflammation can lead to insulin resistance, leptin resistance, increased cortisol levels, and changes in gut bacteria.
As a result, you are hungrier, crave sweets, and store more fat.
While there are more ways inflammation leads to weight gain, we will focus on these four.
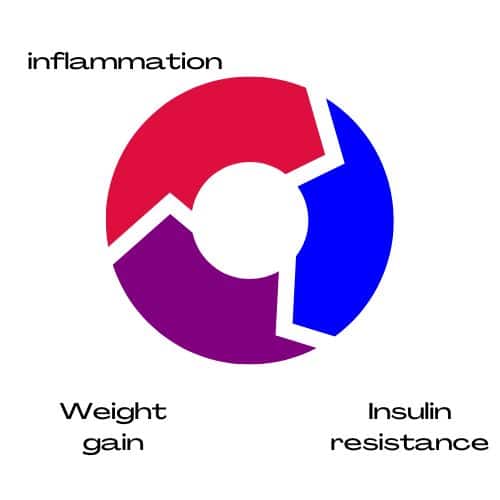
Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and Weight Gain
In response to chronic inflammation, the body releases cytokines. These cytokines can make cells less responsive to insulin. This is called insulin resistance.
When the body is resistant to insulin, it must produce more insulin to stabilize blood sugar levels, resulting in higher insulin levels in the bloodstream. This can increase hunger and fat storage, resulting in weight gain.

Additionally, chronic inflammation can lead to the accumulation of fat cells, particularly in the abdominal area. These fat cells can produce and release inflammatory molecules called adipokines, which can contribute to insulin resistance.
It becomes a cycle, as insulin resistance can also lead to inflammation.
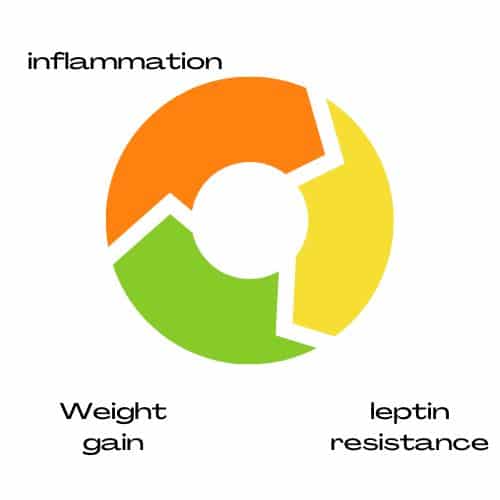
Inflammation, Leptin Resistance, and Weight Gain
When inflammation occurs, it can lead to decreased leptin sensitivity, known as leptin resistance. This means that the body does not receive the signal from the brain to stop overeating, potentially resulting in weight gain over time.
Then, excess weight can lead to further inflammation.
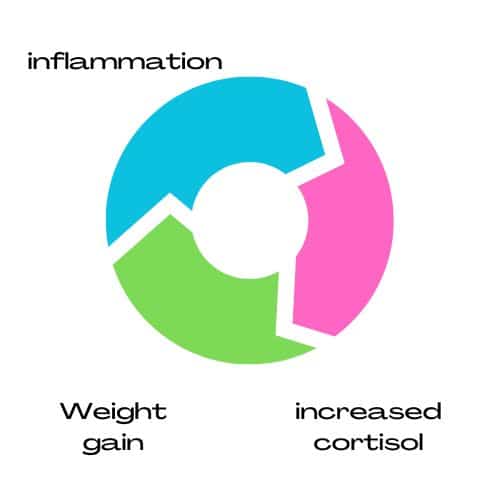
Inflammation, Cortisol, and Weight Gain
Cortisol is a hormone that plays an important role in regulating the stress response in the body.
When inflammation occurs, it can cause the body to release more cortisol, which can lead to weight gain due to increased appetite, cravings, and fat storage.
Studies have shown that higher levels of cortisol are associated with increased waist circumference, a sign of abdominal fat storage.
Moreover, high cortisol levels can interfere with a good night’s sleep, leading to further weight gain.
Inflammation, Gut Health, and Weight Gain
Gut health is integral to overall well-being, and inflammation can have a major impact on it.
Chronic inflammation can lead to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, which comprises billions of bacteria that live in the digestive tract.
When this balance is disrupted, it can increase hunger and cravings, ultimately resulting in weight gain. Additionally, chronic inflammation can lead to increased intestinal permeability, or “leaky gut,” which can also cause weight gain.
The good news is that there are steps you can take to reduce inflammation and get back on track with your health.
How to Fight Inflammation
Here are some tips for reducing chronic inflammation and restoring balance in the body:
- Follow an anti-inflammatory diet: Eating a diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation and support healthy weight management.
- Avoid processed and high-sugar foods: Processed foods and foods high in sugar can contribute to inflammation and weight gain.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Exercise can help reduce inflammation and promote healthy weight management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Get enough sleep: Chronic lack of sleep can contribute to inflammation and weight gain. Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can lead to inflammation and weight gain. Incorporate stress-management techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga into your daily routine.
- Consider supplements: Certain supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and probiotics have anti-inflammatory properties and may support healthy weight management.
Overall, reducing inflammation and preventing weight gain requires a holistic approach that includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and other healthy lifestyle habits.
Get our anti-inflammatory food list here.
The Bottom Line
Inflammation can have a significant impact on our health, including weight gain.
To reduce inflammation and prevent weight gain, it is important to make healthy lifestyle choices such as following an anti-inflammatory diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and considering supplements.
These changes can help restore balance in the body and help to reduce inflammation and support a healthy weight.
With the right steps, you can take control of your health and fight inflammation for good!

Dr. Su-Nui Escobar, a Registered Dietitian/Nutritionist in Miami, FL, is dedicated to empowering women in perimenopause and menopause to live healthier, more satisfying lives.
With a doctorate in clinical nutrition from the University of North Florida, she has expertise in menopause and weight loss, including the unique challenges faced by those on weight loss medications.
Su-Nui’s passion for her field is evident in her previous role as the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics spokesperson.


